Blog
40 C to F: Understanding Temperature Conversion
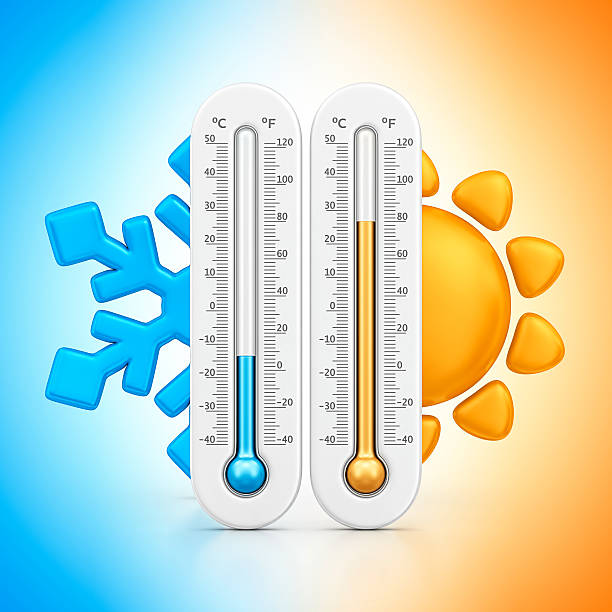

Introduction to Temperature Scales
When discussing temperature , it is essential to understand how different scales relate to each other. Particularly, moving between Celsius (°C) and Fahrenheit (°F) often requires precise knowledge of conversion methods. Therefore, this article explains the process of converting 40°C to °F, delves into the historical background of these scales, and answers common questions about temperature measurement and its applications. Furthermore, we will explore practical examples to enhance understanding.
The Celsius and Fahrenheit Scales
1. What is the Celsius Scale?
The Celsius scale, also referred to as the centigrade scale, is widely used worldwide, particularly in scientific contexts and everyday weather reporting. Moreover, it is named after Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius. The scale is based on two fixed points:
- The freezing point of water (0°C).
- The boiling point of water (100°C).
In addition, it operates on a simple, decimal-based system, making calculations straightforward and accessible.
2. What is the Fahrenheit Scale?
In contrast, the Fahrenheit scale is primarily used in the United States and a few other countries. Developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in the early 18th century, this scale defines:
- The freezing point of water at 32°F.
- The boiling point of water at 212°F.
As a result, the Fahrenheit scale uses a more intricate approach to temperature measurement. However, it remains vital for weather forecasting and industrial applications in certain regions.
How to Convert 40 c to f?
1. The Formula for Conversion
To convert Celsius to Fahrenheit, you can use the following formula:
°F = (°C × 9/5) + 32
Let’s break this down step-by-step for 40°C:
- First, multiply 40 by 9, which equals 360.
- Then, divide 360 by 5, resulting in 72.
- Finally, add 32 to 72, yielding 104.
Thus, 40°C equals 104°F.
2. Why Use This Formula?
The formula reflects the linear relationship between Celsius and Fahrenheit. While the two scales have different starting points and intervals, the formula ensures accurate conversion between them. Consequently, it simplifies the process for both manual and digital calculations.
Applications of Temperature Conversion
1. Everyday Uses
- Cooking: Many recipes, especially those from the U.S., list oven temperatures in Fahrenheit. Consequently, understanding conversions is essential for accurate baking and roasting.
- Travel: When visiting countries that use different temperature scales, knowing how to convert between Celsius and Fahrenheit is extremely helpful. Furthermore, it ensures you are prepared for varying weather conditions.
2. Scientific and Industrial Contexts
- Medicine: Body temperature readings often require conversion, particularly in global healthcare settings. For instance, doctors and nurses may need to convert readings to communicate effectively across regions.
- Engineering: Temperature measurements in mechanical and chemical processes frequently depend on precise conversions between scales. Therefore, engineers rely on accurate data to ensure safety and efficiency.
Historical Insights
1. Origins of the Celsius Scale
Anders Celsius proposed the Celsius scale in 1742. Initially, the scale’s freezing and boiling points were reversed. However, they were later corrected to the format we use today, thereby improving its usability.
2. Development of the Fahrenheit Scale
Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit introduced his scale in 1724, basing it on three reference points:
- The freezing point of a brine solution.
- The freezing point of water.
- The average human body temperature.
Although it differs significantly from Celsius, the Fahrenheit scale remains integral in certain regions due to its historical adoption. Moreover, its continued use highlights the cultural and regional preferences in measurement systems.
FAQs About Temperature Conversion
1. What is the easiest way to convert 40°C to °F?
- Use the formula: (°C × 9/5) + 32. For quick conversions, online tools or calculators are also effective. Additionally, many smartphone apps offer instant temperature conversion features.
2. Why does the U.S. use Fahrenheit instead of Celsius?
- The U.S. adopted Fahrenheit early in its history. Transitioning to Celsius would involve significant changes to industries, weather systems, and public understanding. Furthermore, the Fahrenheit scale’s precision for weather conditions makes it appealing to some users.
3. How accurate is manual temperature conversion?
- Manual calculations using the formula are precise, provided arithmetic errors are avoided. However, digital tools can eliminate the risk of human error.
4. Are there other temperature scales?
- Yes, scales like Kelvin and Rankine are used in scientific and engineering contexts. However, Celsius and Fahrenheit are the most common in daily life.
5. What is the difference between Celsius and Fahrenheit intervals?
- A 1°C change equals a 1.8°F change. Consequently, Fahrenheit has smaller increments, offering more precision for certain applications.
6. How does 40°C compare to average human body temperature?
- The average human body temperature is around 37°C (98.6°F). Therefore, 40°C is considered a high fever or an extremely hot environmental temperature.
7. Why is Celsius preferred in science?
- Celsius aligns with the metric system, making it simpler for scientific calculations. Additionally, its fixed points (freezing and boiling of water) are universally reproducible.
Real-World Examples of 40°C to °F
1. Weather Conditions
- Heatwaves: A temperature of 40°C (104°F) signifies dangerously high heat, commonly experienced in desert regions or during extreme weather events. Consequently, staying hydrated and avoiding prolonged exposure are crucial.
2. Health Scenarios
- Fever: A body temperature of 40°C is a medical emergency, indicating severe fever and requiring immediate attention. Therefore, timely medical intervention is vital.
3. Cooking and Baking
- Oven Temperatures: Some baking recipes might require adjusting Celsius readings to Fahrenheit. For instance, preheating an oven to 40°C would be too low for most dishes but could be part of slow-cooking techniques. Additionally, understanding these conversions ensures culinary precision.
Understanding how to convert temperatures like 40 c to f is not only practical but also essential in a variety of contexts. Moreover, whether for cooking, travel, or scientific applications, mastering this skill enhances clarity and precision. Furthermore, knowing the relationship between Celsius and Fahrenheit scales bridges the gap between different systems, fostering better communication and understanding across diverse fields. Consequently, taking the time to learn these conversions proves beneficial in both everyday and professional scenarios.
Blog
myliberla.com blog: Exploring Innovation, Technology, and Trends

The Evolution of Digital Content
Over the past decade, digital content has undergone significant transformation. From traditional blogs to interactive multimedia experiences, online platforms have continuously adapted to user preferences. With audiences demanding more engaging and informative material, the shift toward high-quality content has been inevitable. This evolution has redefined how businesses and individuals interact with information.
The Role of Blogging in the Digital Age
Blogging has remained a fundamental aspect of digital marketing and personal expression. Despite the rise of video content and podcasts, written articles continue to hold value. A well-maintained blog not only enhances credibility but also contributes to search engine optimization. Informative posts help brands establish authority while providing readers with insightful knowledge.
Why Consistency Matters in Content Creation
Producing consistent content is essential for building a loyal audience. Regular updates keep readers engaged and encourage return visits. Additionally, search engines favor frequently updated websites, improving visibility in search results. By maintaining a steady publishing schedule, a blog remains relevant in an increasingly competitive digital space.
Leveraging SEO for Greater Reach
Search engine optimization (SEO) plays a crucial role in content discovery. Strategic keyword placement, proper structuring, and high-quality backlinks contribute to better rankings. By focusing on on-page and off-page optimization, a blog can attract a broader audience. Furthermore, search engines prioritize valuable and user-friendly content, making SEO an indispensable tool for digital success.
The Impact of AI on Blogging
Artificial intelligence has transformed content creation. AI-driven tools assist in generating topic ideas, optimizing headlines, and even automating writing tasks. While human creativity remains irreplaceable, AI enhances efficiency. Writers can leverage these advancements to streamline their workflow and produce more engaging articles.
Trends Shaping the Future of Blogging
Several emerging trends are shaping the future of blogging. Interactive content, voice search optimization, and personalized recommendations are gaining traction. Readers expect tailored experiences, requiring content creators to adapt. By embracing innovation, bloggers can remain ahead of industry shifts and meet evolving consumer demands.
The Importance of Visual Content
Incorporating images and videos enhances a blog’s appeal. Visual elements break up text, making content more digestible. Additionally, infographics and interactive media improve retention rates. A well-designed blog integrates compelling visuals to complement its written material, fostering a more immersive user experience.
Engaging Audiences Through Social Media
Social media platforms serve as powerful distribution channels for blog content. Sharing articles across multiple networks increases visibility and engagement. Encouraging discussions and responding to comments fosters community interaction. By utilizing social media effectively, bloggers can extend their reach and build lasting relationships with their audience.
Monetization Strategies for Bloggers
Many bloggers turn their platforms into income streams. Sponsored posts, affiliate marketing, and ad placements generate revenue. Membership programs and premium content offerings provide additional monetization opportunities. By diversifying income sources, bloggers can sustain their efforts while delivering valuable content to their readers.
Conclusion: The Future of Blogging
Blogging continues to evolve, adapting to technological advancements and audience preferences. Success in the digital landscape requires consistency, SEO expertise, and engagement strategies. By staying informed about industry trends and leveraging new tools, content creators can thrive in an ever-changing environment. With innovation driving progress, the future of blogging holds limitless possibilities.
Blog
ScoopUpdates.com Is Changing the Way You Follow News

THE DIGITAL NEWS LANDSCAPE IS EVOLVING FAST
ScoopUpdates.com has become a disruptive force in the digital news industry. Readers are expecting more than simply headlines in this day and age, when information is both plentiful and overwhelming. They need valuable insights, well-curated articles, and noise-free real-time updates. To address that demand, ScoopUpdates.com has proactively intervened.
Data-driven storytelling, social media virality, and mobile-first tactics have all influenced the digital news landscape. Despite all of that advancement, transparency and trust are still highly valued. This platform stands out for that reason. ScoopUpdates.com offers more than simply breaking news, in contrast to traditional news aggregators. Rather, it offers readers balance, context, and easily readable summaries so they may remain educated without becoming exhausted.
WHY SCOOPUPDATES.COM STANDS OUT IN A CROWDED FIELD
It’s easy to become lost among the thousands of news portals. However, this platform stands out because to the implementation of various important features. First and foremost, it presents news in an organized and urgent manner. This platform places a higher priority on accuracy and narrative flow than others that focus on sensationalism and fragmentary pieces.
Personalization is also very important. Whether it’s politics, entertainment, technology, business, or global events, users may choose the areas that are most important to them. The webpage then changes to provide a more customized reading experience. Longer engagement and higher satisfaction are encouraged by such a feature.
Furthermore, readers are not left in the dark about the source of the material. Every article is referenced, checked, and connected to trustworthy sources. We don’t consider transparency to be an afterthought.
DAILY DIGESTS THAT EMPOWER, NOT OVERWHELM
Concern over news weariness is rising, particularly as doomscrolling becomes more commonplace. ScoopUpdates.com introduced daily digests as a solution to this problem. The most significant headlines of the day are condensed into a clear and understandable style in these summaries.
With this approach, people with hectic schedules may remain informed without devoting hours to reading the news. Crucially, the digests are written coherently and clearly, utilizing common language that keeps readers rooted in reality.
Additionally, integrating multimedia improves comprehension. There are bullet summaries, charts, infographics, and brief video explainers in place of drawn-out paragraphs. These facilitate understanding of difficult subjects like changes in the economy or geopolitics.
SCOOPUPDATES.COM’S COMMITMENT TO ETHICAL JOURNALISM
Although sensationalism might encourage clicks, it rarely fosters trust. This platform takes a different approach as a result. Stories are guaranteed to be both timely and morally sound by a rigorous editing standards. Unverified assertions and rumors are eliminated.
Before being published, articles go through a rigorous editorial procedure. Updates are released in phases with distinct time stamps and context comments during emergencies or breaking news. This prevents false information without compromising performance.
Underreported stories—those that don’t hit the front page of mainstream media but have social, environmental, or humanitarian significance—are also highlighted by ScoopUpdates.com. This well-rounded strategy promotes a society that is more knowledgeable and compassionate.
THE USER EXPERIENCE: SMOOTH, FAST, AND FOCUSED
The user interface is one of its main advantages. The website is clear and free of distractions and clutter. Readers are kept focused on the material by using simple typeface, sensible classification, and few advertisements. Whether using a desktop, tablet, or mobile device, navigation is simple.
Among the features that enhance the user-friendliness are offline reading, dark mode, and personalized fonts. Transitions are smooth, and pages load quickly. Therefore, the platform accommodates your tastes, regardless of whether you’re a casual reader or a news fanatic.
Push notifications are strategically timed—not incessant pop-ups, but thoughtfully chosen warnings that are important. This well-considered design keeps engagement high and avoids burnout.
INNOVATION THROUGH TECHNOLOGY AND AI INTEGRATION
The platform has incorporated AI technologies in order to remain competitive. Backend algorithms provide tailored article recommendations, trend analysis, and real-time fact-checking. Behind the scenes, these tools make sure that readers always receive accurate and pertinent material.
Additionally, ScoopUpdates.com detects bias and tone using natural language processing. This enables the editorial staff to polish the wording for impartiality and balance. Credibility and user trust have grown as a result of this over time.
Interfaces that rely on chat are also being tried. Users may soon be able to employ interactive AI chatbots to acquire summaries or ask follow-up inquiries. The platform will become even more dynamic and user-friendly as a result.
COMMUNITY ENGAGEMENT AND USER CONTRIBUTIONS
Its community-driven concept is another distinctive aspect. Through user-submitted articles, polls, and comments, readers are invited to become involved. By giving common voices a platform, this democratic layer enriches the news ecosystem.
Additionally, regional forums have been introduced by ScoopUpdates.com to allow people to talk about topics that are pertinent to their communities. While remaining rooted in factual discourse, these venues foster a feeling of community through municipal developments and cultural trends.
Both human editors and computers manage moderation, guaranteeing a civil and educational atmosphere. Disinformation and trolling are dealt with quickly while upholding a high level of engagement.
MULTILINGUAL EXPANSION AND GLOBAL OUTREACH
Although the site started out in English, work to translate it into other languages has already begun. Language restrictions will not prevent non-native English speakers from accessing high-quality content thanks to our global perspective. Local editors either develop native content or translate it.
In addition to language, localization is important. News from regional editions is intimately related to local political and cultural contexts. These editions are substantial and carefully chosen; they are not afterthoughts.
The brand is further strengthened by international collaborations with independent newsrooms. These partnerships are driven by common ideals of impact, openness, and integrity, which guarantee uniformity throughout.
PARTNERING WITH EDUCATORS AND INSTITUTIONS
Collaboration with academic institutions is another significant aspect. Simplified news editions designed for schools are now available to educators. These short stories promote media literacy in young children by introducing them to current events in an approachable way.
Partnerships with universities also give access to validated data sets and analytical tools. The platform can serve as a case study for journalism students studying news formatting, audience involvement, and ethics. As a result, ScoopUpdates.com serves as both an instructional resource and a content outlet.
THE MOBILE APP THAT PUTS NEWS IN YOUR POCKET
The website is only one aspect of accessibility. The mobile application was created to offer a smooth experience while on the go. It appeals to a tech-savvy clientele with features like voice-activated search, customisable alerts, and offline reading.
The app, which is compatible with both iOS and Android, adds mobile-specific benefits without sacrificing editorial quality. The news becomes even more dynamic and captivating with the addition of short-form videos, location-based notifications, and widget integration.
The app also syncs between devices. You may begin reading on your phone and continue precisely where you left off on your tablet. These well-considered features demonstrate the platform’s awareness of contemporary digital practices.
SCOOPUPDATES.COM’S PLAN FOR THE FUTURE
The platform is already making plans for the future as the digital landscape keeps changing. The plan includes decentralized journalism hubs, Web3 integration for content ownership, and blockchain verification for sources. ScoopUpdates.com hopes to lead the news revolution with this progressive approach.
Additionally, the idea of starting a creator fund is being discussed. With the help of this program, independent journalists would have the means to report on important but frequently ignored topics.
The agenda also includes sustainability. To keep its digital footprint as little as possible, the team is investigating carbon offset schemes, ethical advertising strategies, and green hosting options.
FINAL THOUGHTS ON SCOOPUPDATES.COM’S IMPACT
Clarity and trust are more important than ever in a time of short attention spans and information overload. Both are offered by ScoopUpdates.com, along with honesty, accessibility, and customisation. The platform is a movement toward inclusive, knowledgeable, and ethical journalism rather than just another news website.
This platform has become a digital mainstay by accurately presenting pertinent material, using technology to promote transparency, and involve the community at every turn. Its trajectory points to both further expansion and a growing influence on the global news ecosystem.
ScoopUpdates.com is the place to go if you’re looking for the facts without the hype. It has demonstrated that news may be both timely and perceptive, as well as effective and moral. What about that equilibrium? It is the most important thing for readers nowadays.
Blog
Unlocking Global Travel Insights: https://tourism-network.net

The Importance of Tourism Networks
https://tourism-network.net serve as vital platforms for connecting travelers, businesses, and local communities. By fostering collaboration, these networks enhance accessibility, provide insights, and improve travel experiences. With the rise of digital platforms, travelers now benefit from shared knowledge, enabling them to make informed decisions when planning their trips.
How Tourism Networks Benefit Travelers
Tourism networks streamline access to essential travel information. From accommodation recommendations to transport options, travelers gain valuable insights. Additionally, these networks facilitate cultural exchange by connecting tourists with local communities, enriching their overall experience.
Role of Digital Platforms in Tourism
Digitalization has transformed the way tourism networks operate. Online platforms offer real-time updates, destination guides, and user-generated content. Virtual communities enable travelers to share experiences, receive recommendations, and access exclusive travel deals. The availability of mobile applications further enhances accessibility, making it easier for tourists to navigate their destinations.
Sustainable Tourism and Community Involvement
Sustainability plays a crucial role in modern tourism. Networks promote responsible travel by encouraging eco-friendly practices and supporting local economies. Community-based tourism initiatives ensure that cultural heritage is preserved while providing employment opportunities. By participating in these networks, travelers contribute positively to environmental conservation and local development.
How Businesses Benefit from Tourism Networks
Tourism-related businesses leverage these networks for increased visibility. Hotels, tour operators, and transport services can reach a broader audience through digital marketing strategies. Additionally, customer feedback helps businesses refine their services, ensuring customer satisfaction. Partnerships formed within tourism networks contribute to mutual growth and industry development.
Tips for Maximizing Travel Experiences
- Join reputable tourism networks for reliable information
- Research destinations through user-generated reviews and expert recommendations
- Utilize digital platforms for itinerary planning and real-time updates
- Engage with local communities to gain authentic cultural experiences
- Support sustainable tourism initiatives by choosing eco-friendly options
Future of Tourism Networks
The integration of artificial intelligence and data analytics is set to revolutionize tourism networks. AI-driven recommendations will offer personalized travel experiences, while blockchain technology ensures secure transactions. As technology advances, these networks will become more efficient, creating seamless experiences for travelers worldwide.
FAQs
What is a tourism network?
- A tourism network is a collaborative platform connecting travelers, businesses, and local communities to enhance travel experiences.
How do tourism networks help travelers?
- They provide valuable travel insights, recommendations, and real-time updates, making trip planning more convenient.
Are tourism networks beneficial for businesses?
- Yes, businesses gain visibility, customer engagement, and networking opportunities through these platforms.
How can travelers contribute to sustainable tourism?
- By supporting local businesses, practicing eco-friendly habits, and engaging in responsible tourism activities.
What are the latest trends in tourism networks?
- AI-driven personalization, blockchain-based transactions, and virtual reality travel experiences.
-

 Health6 months ago
Health6 months agoUnlocking Knowledge and Wellness: Exploring the Vital-Mag.net Blog
-

 Apps6 months ago
Apps6 months agoMangaBuddy: Your Gateway to Unlimited Manga Adventures
-

 News5 months ago
News5 months agoKristen Archives: Exploring a Treasure Trove of Online Stories
-

 Crypto6 months ago
Crypto6 months agoCrypto30x.com Gigachad: Redefining Cryptocurrency Success
-
 Apps6 months ago
Apps6 months agoHomeworkify: Revolutionizing the Way Students Approach Assignments
-

 Apps6 months ago
Apps6 months agoSimpCity: Exploring a Unique Online Community
-

 Health7 months ago
Health7 months agoExploring the Mega-Personal.net Health Archives: A Treasure Trove of Information
-

 Apps5 months ago
Apps5 months agoTraceLoans.com Business Loans: Empowering Entrepreneurs with Financial Solutions
