Research
Research Companies Papa Johns
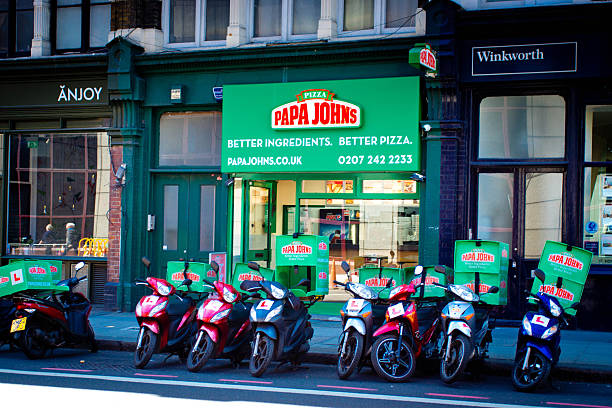

Research Companies Papa Johns International, Inc., a globally recognized pizza chain, has built its reputation on the promise of “Better Ingredients. Better Pizza.” From its humble beginnings in a broom closet to becoming one of the world’s largest pizza delivery companies, Papa John’s offers valuable insights into business growth, branding, and customer loyalty. This article explores Papa John’s history, business strategy, key offerings, and why it serves as an excellent subject for research.
The History of Papa John’s
Humble Beginnings
Papa John’s was founded in 1984 by John Schnatter in Jeffersonville, Indiana. The business began with Schnatter selling pizzas out of a converted broom closet in his father’s tavern. With a focus on quality ingredients, the venture quickly gained traction.
Rapid Expansion
By the late 1980s, Papa John’s had expanded beyond its local roots, opening franchises across the United States. Its commitment to high-quality pizza and innovative marketing helped the company stand out in a crowded market.
Going Global
Papa John’s became a publicly traded company in 1993, fueling its expansion into international markets. Today, the company operates in over 40 countries, with thousands of locations worldwide.
Papa John’s Business Model
Papa John’s success is rooted in a franchise-based model that emphasizes quality, innovation, and customer satisfaction. Key components of the business model include:
1. Focus on Quality
Papa John’s differentiates itself through its use of high-quality ingredients, including fresh dough, vine-ripened tomatoes, and 100% mozzarella cheese. This focus on quality is central to its branding and customer appeal.
2. Franchise-Driven Growth
The majority of Papa John’s stores are franchises, allowing the company to expand rapidly while minimizing overhead costs. Franchisees are supported with training, marketing tools, and supply chain management.
3. Technology Integration
Papa John’s was one of the first pizza chains to embrace online ordering, launching its digital platform in 2001. This early adoption of technology gave the company a competitive edge in convenience and customer experience.
4. Customer-Centric Approach
From loyalty programs to promotional deals, Papa John’s prioritizes customer satisfaction. The “Papa Rewards” program incentivizes repeat business, fostering customer loyalty.
Key Offerings of Papa John’s
Papa John’s menu caters to a wide range of tastes and preferences. Its product portfolio includes:
1. Pizzas
The flagship offering includes a variety of pizzas made with premium ingredients. Customers can choose from classic options like pepperoni and cheese or specialty pizzas such as BBQ Chicken Bacon or Garden Fresh.
2. Sides and Appetizers
The menu includes items like breadsticks, chicken wings, and garlic knots, providing customers with complementary options for a full meal.
3. Desserts
Sweet treats like Chocolate Chip Brownie and Cinnamon Pull-Aparts are popular choices among customers.
4. Customizable Options
Papa John’s allows customers to customize their orders with various crusts, toppings, and sauces, enhancing the overall dining experience.
Marketing Strategies of Papa John’s
Papa John’s has employed innovative marketing strategies to establish and maintain its brand identity:
1. “Better Ingredients. Better Pizza.”
This slogan encapsulates the brand’s commitment to quality and has been central to its advertising campaigns since the company’s inception.
2. Sports Sponsorships
Papa John’s has partnered with major sports leagues and events, including the NFL and NASCAR, to increase brand visibility and connect with a broader audience.
3. Digital Marketing
The company leverages social media platforms and email marketing to engage with customers, promote new products, and share exclusive deals.
4. Loyalty Programs
The Papa Rewards program offers points for every purchase, which can be redeemed for free menu items. This initiative fosters repeat business and customer loyalty.
The Role of Technology in Papa John’s Success
Papa John’s has been a pioneer in integrating technology into its operations:
1. Online and Mobile Ordering
The company’s robust digital platform allows customers to place orders quickly and easily. Mobile apps and websites are user-friendly, offering features like real-time tracking and saved orders.
2. AI and Data Analytics
Papa John’s uses data analytics to understand customer preferences, optimize delivery routes, and enhance operational efficiency. AI-powered systems support personalized marketing and menu recommendations.
3. Innovative Delivery Solutions
From no-contact delivery options to partnerships with third-party services like Uber Eats and DoorDash, Papa John’s continuously evolves to meet customer needs.
Papa John’s Global Presence
Papa John’s operates in over 40 countries, with key markets including:
1. North America
The United States remains Papa John’s largest market, with a significant presence in Canada as well.
2. Europe
Countries like the United Kingdom and Spain are strongholds for the brand in the European market.
3. Asia-Pacific
Papa John’s has expanded into countries like China, South Korea, and India, tapping into the region’s growing demand for international cuisines.
4. Middle East and Africa
In markets like Saudi Arabia and the UAE, Papa John’s has tailored its offerings to suit local tastes while maintaining its core brand identity.
Sustainability and Corporate Responsibility
Papa John’s recognizes the importance of sustainability and community engagement:
1. Sustainable Sourcing
The company works to ensure its ingredients are ethically sourced, with a focus on reducing environmental impact.
2. Reducing Waste
Papa John’s has implemented measures to minimize food and packaging waste, including the use of recyclable materials.
3. Community Involvement
The Papa John’s Foundation supports education, food insecurity programs, and disaster relief efforts.
4. Diversity and Inclusion
The company promotes diversity within its workforce and partners with organizations that advocate for equality and social justice.
Challenges Facing Papa John’s
Like any major company, Papa John’s faces challenges, including:
1. Intense Competition
The pizza industry is highly competitive, with brands like Domino’s and Pizza Hut vying for market share.
2. Evolving Consumer Preferences
Health-conscious consumers are driving demand for healthier menu options, requiring Papa John’s to innovate continually.
3. Economic Pressures
Fluctuating ingredient costs and labor expenses can impact profitability.
4. Brand Image
Past controversies have occasionally affected the company’s reputation, necessitating efforts to rebuild trust with consumers.
Why Papa John’s Is a Valuable Research Subject
For businesses, students, and researchers, Papa John’s offers insights into:
- Brand Differentiation: How to stand out in a competitive market through quality and innovation.
- Technology Integration: The role of digital tools in enhancing customer experience and operational efficiency.
- Global Strategy: Balancing local adaptation with maintaining a consistent global brand.
- Resilience: Lessons in overcoming challenges and navigating controversies.
The Future of Papa John’s
Looking ahead, Papa John’s aims to strengthen its market position through:
1. Menu Innovation
Introducing new flavors, healthier options, and limited-time offers to attract diverse customer segments.
2. Digital Transformation
Continuing to invest in AI, data analytics, and delivery solutions to improve customer convenience and satisfaction.
3. Global Expansion
Exploring untapped markets while deepening its presence in existing regions.
4. Sustainability Leadership
Enhancing its commitment to environmentally friendly practices and corporate social responsibility.
Conclusion: A Recipe for Success
Papa John’s journey from a small pizza shop to a global powerhouse is a testament to the power of quality, innovation, and customer focus. Its business strategies, marketing initiatives, and resilience in the face of challenges make it a fascinating subject for research.
For those studying branding, franchising, or the food service industry, Papa John’s offers valuable lessons in building a successful, customer-centric business. As the company continues to evolve, it remains a shining example of how passion and perseverance can lead to global success.
Research
Behind the Scenes: The Craftsmanship of Red Wing Shoes in Potosi, MO

Introduction to Red Wing Shoes and their History
Step into the world of craftsmanship, where tradition meets innovation. Red Wing Shoes has long been a name synonymous with quality footwear, and for good reason. With roots dating back over a century, this iconic brand began its journey in 1905, aiming to provide workers with durable shoes that could withstand the rigors of everyday life. Fast forward to today, and one of their proudest production facilities is nestled in Potosi, MO.
This factory is more than just a place of work; it’s a hub of artistry and precision. Here, every shoe tells a story—a tale woven from skilled hands and high-quality materials. Join us as we take you behind the scenes at Red Wing Shoes in Potosi, MO. Discover how passion transforms into craftsmanship and why these shoes have earned their revered status among consumers everywhere.
The Potosi Factory: A Look at the Production Process
Nestled in the heart of Potosi, Missouri, the Red Wing Shoes factory stands as a testament to American craftsmanship. Here, every shoe begins its journey with meticulous planning and design.
The production process is intricate and involves numerous steps. It starts with selecting high-quality leather sourced from trusted suppliers. Each hide is carefully inspected for imperfections before it moves on to cutting.
Skilled hands expertly shape each component of the shoe. Precision is key—every cut must be exact to ensure both beauty and functionality. Afterward, components are assembled using time-honored techniques.
The factory hums with activity as craftsmen work side by side. Their expertise shines through in every stitch they make. Hand-sewing remains a vital aspect, maintaining that personal touch in an era dominated by automation.
Here at this facility, tradition meets innovation seamlessly—each pair tells a story rooted deep within the community’s heritage.
The Importance of Quality Materials in Crafting Red Wing Shoes
Quality materials are the backbone of Red Wing Shoes. Every pair begins with meticulously sourced leather, chosen for its durability and character. This commitment to high-quality materials ensures that each shoe not only looks exceptional but also withstands the test of time.
The selection process is rigorous. The team inspects hides for imperfections, ensuring that only the finest make it into production. This attention to detail translates into shoes that mold beautifully to your feet over time.
Beyond leather, other components like stitching threads and soles are carefully selected. Each element plays a vital role in overall performance and longevity.
It’s this dedication to using top-tier materials that sets Red Wing apart from ordinary footwear brands in Potosi, MO. Each shoe tells a story of craftsmanship and quality that resonates with wearers across generations.
The Art of Hand-Sewing: Meet the Skilled Craftsmen and Women behind the Shoes
At the heart of Red Wing Shoes in Potosi, MO, lies a rich tradition of hand-sewing. This meticulous process sets these boots apart from mass-produced footwear. Skilled craftsmen and women pour their expertise into every stitch.
Each artisan brings years of experience to the table. Their hands expertly manipulate needles and thread, crafting shoes that are both functional and beautiful. The precision involved is remarkable; one misstep could compromise the integrity of the shoe.
Beyond technique, there’s an artistry to this work that transcends mere production. Every seam tells a story—of dedication, skill, and passion for quality craftsmanship.
The artisans take immense pride in their creations. For them, it’s not just about making shoes; it’s about preserving a legacy steeped in history while adapting to modern needs. Each pair reflects individuality shaped by human touch rather than machinery alone.
Sustainability and Ethical Practices at Red Wing Shoes
Red Wing Shoes in Potosi, MO, takes sustainability seriously. The brand prioritizes eco-friendly materials and practices at every stage of production.
They source leather from tanneries that adhere to strict environmental standards. This ensures that the tanning process minimizes harmful waste while preserving quality.
The factory itself embraces energy efficiency, utilizing modern technologies to reduce its carbon footprint. By investing in renewable energy sources, Red Wing Shoes is committed to a greener future.
Ethical labor practices are equally crucial. Workers enjoy fair wages and safe working conditions, reflecting the company’s dedication to social responsibility.
Moreover, the brand focuses on crafting long-lasting footwear. High-quality products mean less frequent replacements, reducing overall waste over time.
This commitment resonates with consumers who value both style and substance in their purchasing decisions.
From Factory to Foot: How Red Wing Shoes Ensure Comfort and Durability for Customers
Red Wing Shoes in Potosi, MO, takes pride in a meticulous production process that emphasizes comfort and durability. Each pair of shoes is crafted with the wearer’s experience in mind.
The design phase incorporates customer feedback. This ensures that styles align perfectly with the needs of various professions and lifestyles. The team pays attention to every detail— from arch support to moisture-wicking linings.
Once designed, high-quality materials are sourced for their resilience. Premium leather combined with sturdy soles creates footwear that withstands daily wear while providing optimum comfort.
Quality control checks occur at every stage of production. Craftsmen ensure each shoe meets stringent standards before it reaches the consumer’s hands.
It’s this dedication to craftsmanship that transforms Red Wing Shoes into long-lasting companions for countless adventures on and off the job site.
Conclusion: The Timeless Appeal of Red
The craftsmanship behind Red Wing Shoes in Potosi, MO is a blend of history and innovation. Each pair embodies decades of tradition while embracing modern techniques. The artisans pour their skills and passion into every stitch, ensuring that each shoe not only meets but exceeds expectations.
Quality materials are at the heart of this process. From premium leathers to robust soles, the focus on durability shines through in every step of production. This dedication doesn’t just create shoes; it builds trust with customers who know they can rely on their footwear.
Sustainability is woven into the fabric of Red Wing’s ethos. Ethical sourcing practices ensure that both people and planet are respected throughout the manufacturing process. This commitment resonates with consumers who value responsible brands.
Wearing Red Wing Shoes means stepping into a legacy defined by comfort and endurance. The careful attention given to fit enhances not just how they look but how they feel during daily wear.
With roots firmly planted in skilled craftsmanship, time-honored traditions, and forward-thinking approaches to sustainability, Red Wing Shoes continues to captivate those seeking quality footwear that stands the test of time. The appeal lies not just in what you see but also in what you experience when wearing them—each step tells a story steeped in heritage and artistry.
Research
Ferrari in Formula 1: The Unmatched Pursuit of Racing Excellence
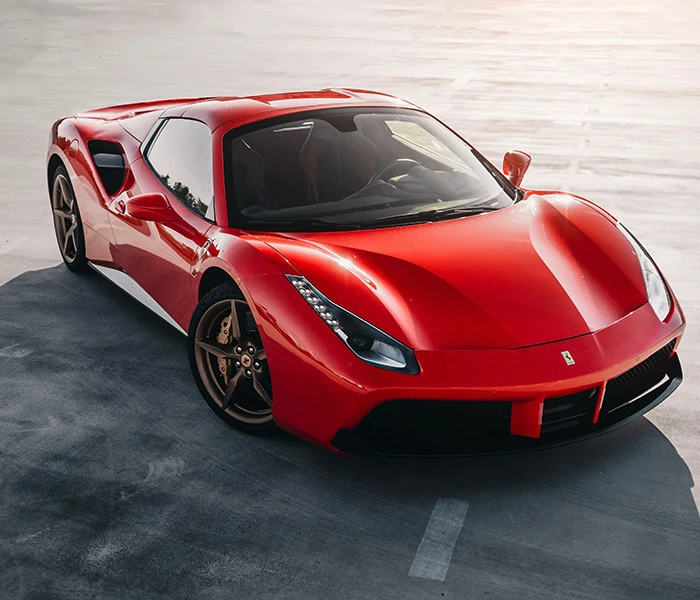

Introduction to Ferrari and Formula 1 Racing
Ferrari – a name that resonates with speed, luxury, and an unparalleled legacy in the world of motorsport. Since its inception, this iconic brand has carved out a unique niche in Formula 1 racing. With each roar of their engines, fans are reminded of the passion and precision that define not just a car but an entire philosophy towards racing.
The allure of Ferrari lies not only in its stunning design but also in its relentless pursuit of excellence on the track. For decades, it has captivated audiences worldwide with thrilling performances and fierce rivalries. Whether you’re new to F1 or a lifelong fan, understanding Ferrari’s journey through the sport is essential for grasping what makes this team so extraordinary.
Join us as we delve into the rich history and remarkable achievements that have solidified Ferrari’s status as one of the greatest forces in Formula 1 racing. Get ready to explore their innovative spirit, legendary drivers, and enduring legacy that continues to inspire generations both on and off the track.
The History of Ferrari in Formula 1
Ferrari’s journey in Formula 1 began in 1950, the inaugural year of the championship. The iconic prancing horse quickly became a symbol of speed and performance. Enzo Ferrari’s vision was clear: to create cars that weren’t just fast but also technologically advanced.
Throughout the decades, Ferrari experienced remarkable highs and challenging lows. They secured their first World Championship title with Giuseppe Farina in 1950. But it wasn’t just about winning; it was about passion and craftsmanship.
The team dominated much of the 1960s and ’70s under legends like Niki Lauda. His fierce determination led to three championships during a golden era for Ferrari.
However, every success came with setbacks—tragedies both on-track and off were part of their story too. Yet, through perseverance, Ferrari has remained resilient, continually evolving while staying true to its racing roots.
The Key Players: Drivers, Engineers, and Team Management
Ferrari’s success in Formula 1 is shaped by its key players. The drivers embody the heart and soul of the team. Legends like Michael Schumacher and Kimi Räikkönen have left indelible marks on Ferrari’s legacy, pushing boundaries with their extraordinary skill.
Behind these exceptional athletes are brilliant engineers dedicated to innovation. They work tirelessly to develop cutting-edge technology, enhancing speed and safety on the track. Their expertise transforms bold concepts into high-performance machines that roar down circuits worldwide.
Team management plays a crucial role as well. Visionary leaders unite diverse talents, ensuring seamless communication and collaboration among all facets of the organization. This synergy fosters an environment where creativity thrives, paving the way for groundbreaking strategies during intense races.
Together, these elements create a powerful ecosystem that drives Ferrari towards unparalleled achievements in racing history. Each member contributes to a shared dream: dominating Formula 1 while honoring tradition and pursuing excellence relentlessly.
Technological Innovations and Advancements Made by Ferrari
Ferrari has consistently pushed the boundaries of technology in Formula 1. From their groundbreaking aerodynamics to advanced hybrid power units, innovation is at the heart of their racing philosophy.
One notable advancement is the development of the F1-75 car. It showcased a unique sidepod design that enhanced airflow efficiency and overall performance. This attention to detail allows them to maximize speed while maintaining control.
Furthermore, Ferrari’s commitment to integrating artificial intelligence into race strategy offers a competitive edge. Real-time data analysis during races helps optimize tire choices and pit stops, ensuring they stay ahead of rivals.
The team also invests heavily in materials science, utilizing lightweight composites that improve vehicle agility without compromising safety. Every improvement reflects Ferrari’s relentless pursuit of excellence on the track.
These technological strides not only elevate Ferrari but also set benchmarks for competitors across the grid.
Challenges Faced by Ferrari in the World of Formula 1
Ferrari, despite its illustrious history, has faced numerous challenges in the fiercely competitive world of Formula 1. One significant hurdle is maintaining consistent performance amid rapidly evolving technology. Other teams innovate at lightning speed, leaving Ferrari to constantly adapt.
Managing driver expectations also presents a unique challenge. With immense pressure to perform, even top-tier drivers can struggle under scrutiny from fans and media alike. Balancing team dynamics becomes crucial.
Moreover, strategic decisions during races often lead to criticism if outcomes aren’t favorable. Mistakes in pit stops or tire choices can cost valuable points and championships.
The financial aspect cannot be overlooked either. While Ferrari enjoys a robust budget compared to many other teams, increasing costs associated with research and development strain resources further.
Navigating regulatory changes imposed by governing bodies adds another layer of complexity that demands agility and foresight from the entire organization.
The Legacy of Ferrari in Formula 1 Racing
Ferrari’s legacy in Formula 1 is a rich tapestry woven with triumphs and tragedies. Since their debut in the championship, they have become synonymous with speed, passion, and unparalleled craftsmanship.
The iconic prancing horse symbolizes not just a car but an era of racing excellence. With numerous Constructors’ Championships and Drivers’ titles under their belt, Ferrari has set benchmarks that many aspire to achieve.
Legends like Michael Schumacher reshaped the sport while donning the red overalls. Their impact transcended mere statistics; it ignited dreams for countless fans around the globe.
Even amidst fierce competition, Ferrari’s distinctive approach—merging tradition with innovation—ensures its place at motorsport’s pinnacle. The roar of their engines echoes through history as a testament to dedication and relentless pursuit of perfection.
Every race season adds another layer to this storied saga, making every moment significant within both automotive history and sporting culture.
Conclusion: Why Ferrari Remains a Dominant Force in the Sport
Ferrari’s presence in Formula 1 is nothing short of legendary. Their rich history, marked by triumphs and challenges alike, has shaped the landscape of motorsport. The drivers who have donned the iconic red suit are not just athletes; they are part of a compelling narrative that includes passion, precision, and performance.
The engineering prowess behind Ferrari sets them apart from their competitors. Innovative technologies developed over decades have propelled them to new heights on the racetrack. These advancements do not merely enhance speed but also push the boundaries of what is possible in automotive design.
Yet it’s not just about technology or talent. Team management plays an essential role in maintaining harmony and focus within this high-pressure environment. The synergy among drivers, engineers, and strategists creates a formidable force that continuously adapts to ever-changing circumstances.
Despite facing numerous challenges—be it fierce competition or regulatory changes—Ferrari’s resilience shines through. Each setback offers lessons learned, propelling them forward with renewed determination.
As one looks ahead at Formula 1’s future, Ferrari remains uniquely positioned as both a legacy brand and an innovator ready to tackle whatever comes next. Their unwavering commitment to excellence ensures that they will continue making headlines for years to come in this thrilling sport where every second counts.
Health
Exploring the Mega-Personal.net Health Archives: A Treasure Trove of Information
Mega-personal.net health archives is widely known as a versatile online platform, offering a variety of features and tools for its users. One of the hidden gems of this website is its Health Archives, a robust repository of articles, resources, and insights related to wellness and healthcare. This article delves into the importance, structure, and benefits of the Mega-Personal.net Health Archives, showcasing why it has become a go-to source for health-conscious individuals.
-

 Health7 months ago
Health7 months agoUnlocking Knowledge and Wellness: Exploring the Vital-Mag.net Blog
-

 Apps7 months ago
Apps7 months agoMangaBuddy: Your Gateway to Unlimited Manga Adventures
-

 News5 months ago
News5 months agoKristen Archives: Exploring a Treasure Trove of Online Stories
-

 Crypto6 months ago
Crypto6 months agoCrypto30x.com Gigachad: Redefining Cryptocurrency Success
-
 Apps7 months ago
Apps7 months agoHomeworkify: Revolutionizing the Way Students Approach Assignments
-

 Apps6 months ago
Apps6 months agoSimpCity: Exploring a Unique Online Community
-

 Health7 months ago
Health7 months agoExploring the Mega-Personal.net Health Archives: A Treasure Trove of Information
-

 Apps6 months ago
Apps6 months agoTraceLoans.com Business Loans: Empowering Entrepreneurs with Financial Solutions
